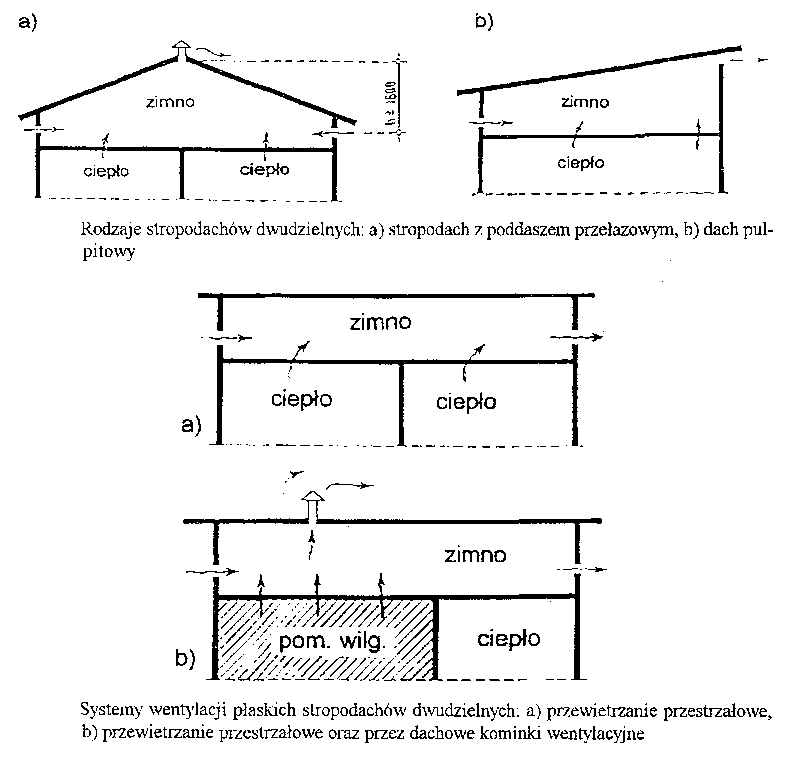
 Bipartite roofs best protect residential interiors against excessive heat loss, moisture and overheating. They are recommended especially above rooms with water vapor pressure above 2130 Well. In double-section flat roofs, the air space above the insulated ceiling under the roofing structure is usually several dozen centimeters high., and sometimes over 1m (man-pass roofs), thanks to which there is a more free exchange of air between the ventilated space and the outside air.
Bipartite roofs best protect residential interiors against excessive heat loss, moisture and overheating. They are recommended especially above rooms with water vapor pressure above 2130 Well. In double-section flat roofs, the air space above the insulated ceiling under the roofing structure is usually several dozen centimeters high., and sometimes over 1m (man-pass roofs), thanks to which there is a more free exchange of air between the ventilated space and the outside air.
The drawings show different ways of ventilating flat roofs with different shapes of the attic. Ventilation is that, "Pumped" by the wind pressure through the inlet openings, the air from the ventilated space is displaced along with the water vapor through the outlet openings to the outside by the suction of the wind. Ventilation slots during the summer, allowing air movement under the roof covering, they discharge heated air from the attic space and thus reduce the roof temperature. Strong wind pressure on the external partition of the roof promotes good ventilation. As the wind pressure increases, the air stream flows faster.
Ventilation rules
1. The movement of air in the ventilated air space of the flat roof can be caused by the interaction of the wind between the air inside the ventilated space and the air outside, which causes a pressure difference causing convective air movement.
2. The location of the air supply and exhaust openings in the flat roof depends on this, what is the induced air movement and the shape and dimensions of the ventilated space .
3. In bipartite flat roofs with an air space of more than 20 cm distance between the inlet and outlet openings may reach 25-30 m.
4. In flat roofs with low air space (do 20 cm) the distance between these holes may be max 12-15 m.
5. The air space should always be located above the thermal insulation layer.
6. When locating the outer longitudinal walls of the building in the north-south direction, ventilation should be caused by the temperature difference, in this case, the difference in heights of air inlets and outlets should be kept as high as possible.
7. When locating longitudinal walls in the east-west direction, ventilation should be caused by wind pressure, then the vents on- and exhaust must be placed 5-10 cm above the thermal insulation layer.
8. Ventilation openings should be located under the cornice or eaves.
9. It is advisable to use ventilation openings in the form of a continuous slot or in the form of evenly distributed openings (e.g. with perforated brick, ceramic filters, etc.); when using larger holes, the distance should not exceed them 1,0 m.
The efficiency of the ventilation largely depends on the decomposition (mutual location of the building), the shape and total area of the inlet and outlet openings. For the ventilation system to work properly, the area of the inlet openings (supply air) must be equal to or greater than the area of the outlet openings (exhaust air). A properly constructed ventilation system uses the "principle of raising warm air". The air flow direction is most often in line with the roof slope, thus, in addition to the wind pressure, a natural gravity thrust is created. It facilitates the movement of air under the roof slope, even in windless weather. According to the existing Polish guidelines, the area of ventilation openings should be no less than 1/1000 flat roof surface, tj. 10 cm2 for each m2 of the ventilated roof area.
The current regulations specify the minimum areas of openings between the air layer inside the flat roof and the outside air. For a well-ventilated horizontal air layer, the minimum area of openings is 15 cm2 for each m2 of the flat roof surface. In the case of flat roofs, this area should be related to the area of roof slopes. Thus, the area of the inlet openings (supply air) and outlet openings (exhaust air) must be calculated separately for the entire roof area. For comparison – in the USA is required, that the total area of the vents (supply and exhaust) was min. 1/150 attic ceiling area. However, in buildings with a vapor barrier layer, it should be min. 1/300 floor surface