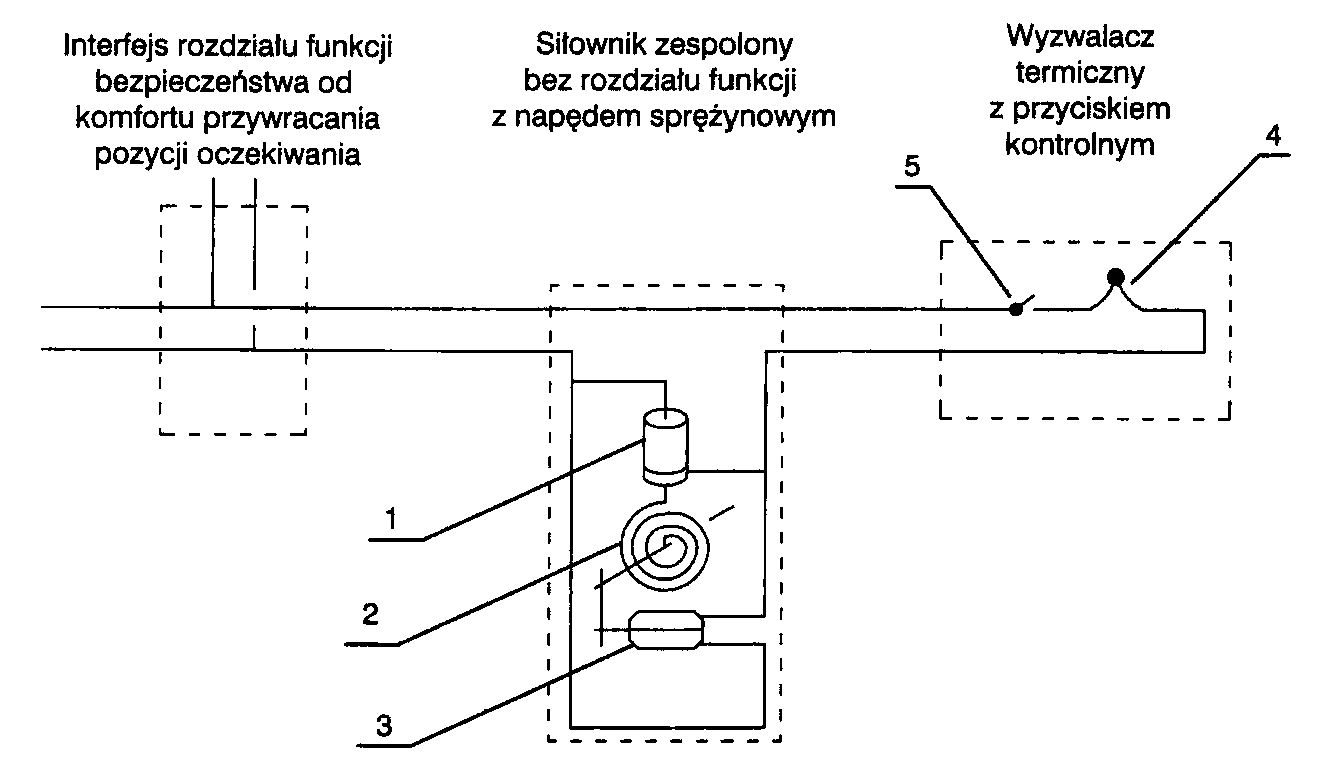
 Diagram showing the principle of actuating a complex actuator "without separation of functions" with a spring actuator. 1. Electromagnetic clutch or bolt, 2. Spring drive, 3. Electric engine, 4. Thermal trigger, 5. Thermal button.
Diagram showing the principle of actuating a complex actuator "without separation of functions" with a spring actuator. 1. Electromagnetic clutch or bolt, 2. Spring drive, 3. Electric engine, 4. Thermal trigger, 5. Thermal button.
In case of, when the transition to the damper's safety position and its return to the waiting position is ensured by a combined electromechanical rotary actuator equipped with a spring drive, we say, that it is a control mechanism "without separation of safety functions" from the comfort functions of restoring the standby position. The spring drive of the actuator remains tight during normal operation of the ventilation and air conditioning system, thus storing the potential energy necessary to close the damper. It is locked in this position by an electromagnetic release (via a bolt or clutch), which is continuously energized. A thermal release is serially connected to the electromagnetic release circuit – microswitch with heavy bimetal or based on low-melting bismuth alloys, additionally equipped with a test button with a normally closed contact. The actuator's spring drive actuation occurs as a result of a power interruption to the electromagnetic release and is possible in three cases:
– temperature rise above the activation temperature of the thermal release,
– pressing the control button manually,
– control signal from the CSP – power supply interruptions.
Activation of the spring drive releases the accumulated potential energy and closes the damper. The closing time of the partition in this type of mechanisms is up to 30 s. Return the flap to the waiting position – its opening, occurs as a result of the spring drive being stretched by the electric motor which is an integral part of the actuator, after restoration of continuous electrical power. In most cases, limit switches are also built inside the actuator, which signal the beginning and end of each change of the damper partition position. Use of a signal in the form of a current interruption to control fire dampers equipped with a "no function separation" control mechanism with spring actuation, means, that in the event of a power failure in the power supply system, they will be closed. In such a situation, the movement of the dampers to the safety position in the zone covered by the fire is therefore an activity preceding the possible reaction of the SAP systems. However, closing the dampers outside the hazardous zone excludes the possibility of implementing the scenario of the development of events during a fire, presented in the Guide. In connection with, using the discussed control mechanisms, it is necessary to protect electric circuits and uninterruptible power supply separately for each fire zone. This will significantly reduce the risk of closing the dampers outside the fire zone. Control of fire dampers with a "non-functional separation" control mechanism with spring actuation, should take place via interfaces that allow separation of safety functions from the comfort of restoring a waiting position, which should be installed on the damper or in its immediate vicinity. The interface for the distribution of functions in the field of control enables and guarantees the actuation of the safety position of the flaps from the CSP level, that the waiting position can only be restored after the zone circuit breaker is actuated, in which the inspection was made (intervention). In this way, the obligation to verify by the facility security services each fire hazard signal in place will be enforced, from which this signal comes, before the normal functioning of the CSP is restored.