Buildings of the ZL category
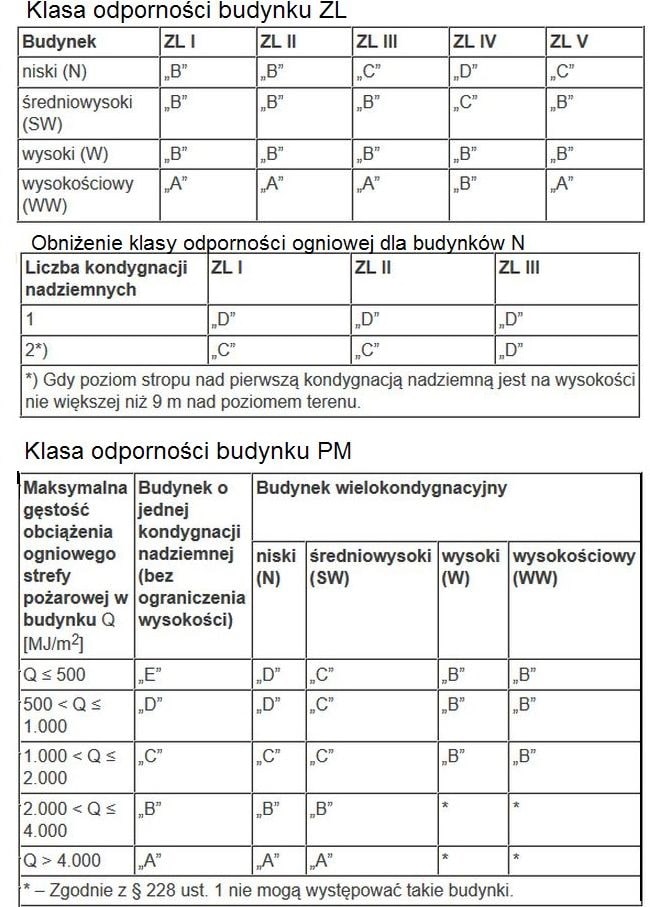
According to the division of buildings according to their purpose and method of use, residential buildings, collective residence and public utility buildings as well as parts of buildings constituting separate fire zones, is characterized by the appropriate risk category for humans, referred to as ZL:
1) ZL I – containing rooms intended for simultaneous presence above 50 non-regular users, and not primarily intended for use by people with reduced mobility,
2) ZL II – intended primarily for use by people with reduced mobility, such as hospitals, nurseries, before school, homes for the elderly,
3) ZL III – public utility not qualified for ZL I and ZL II,
4) ZL IV – residential,
5) ZL V – collective residence not qualified for ZL I and ZL II.
In the event that the fire zone, due to the purpose and method of use, it is included in more than one human hazard category, then it should meet the requirements specified for each of these categories.
Public utility buildings are generally accessible buildings intended, inter alia, for public administration, culture, education, healthcare and services, as well as all office and social buildings. On the other hand, buildings of collective residence are buildings intended for temporary stay of people outside their permanent place of residence .
Behind the tall building (W) a building with a height of more than 25 m do 55 m above ground level, inclusive, or residential over 9 do 18 above-ground storeys, inclusive, while for a high-rise building (WW) – a building with a height above 55 m above ground level. The above building height is calculated from the ground level at the lowest entrance to the building or its part, to the upper plane of the ceiling or the highest edge of the flat roof above the highest usable floor, including the thickness of the thermal insulation and the covering layer, or to the uppermost top face of another covering. Appropriate evacuation conditions should be provided from every place intended for people to stay in the facility, consisting in, inter alia, securing the evacuation routes listed in technical and construction regulations against smoke, including: on the use of smoke prevention devices or devices and other technical and construction solutions ensuring smoke removal. The protection against smoke on the escape routes is considered to be protection against the persistence of smoke on the escape routes in the amount of, which is due to reduced visibility or toxicity, would prevent safe evacuation.